In March 2023, the world came together at the United Nations Water Conference 2023, convened by the United Nations General Assembly. The outcome of this conference is the “Water Action Agenda“, which has been materialized through various commitments, pledges, and actions. The document “Engineering, Groundwater, and Integrated Water Resources Management” (available here) is WFEO’s first commitment to the “Water Action Agenda”.
This publication, drafted by the WFEO Committee on Water (CW), provides a comprehensive perspective of groundwater in the context of integrated water resources management and in the framework of the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
CW covers all WFEO initiatives in water engineering and its relations with United Nations bodies and agencies, mainly with UN-Water and UNESCO. Its activity is framed within the scope of the contribution of engineering to Sustainable Development Goals.
Water, as a prerequisite for life, is a critical resource and assumes a special focus in terms of sustainable development and its management faces major challenges related to climate change and human activities.
Groundwater is the most abundant source of freshwater on earth, accounting for approximately 99%, and is a sustainable and affordable source of drinking water especially for rural populations in most parts of the world. Due to the fact that the soil constitutes an immense natural filter many aquifers provide water that requires no treatment other than disinfection. This aspect is very important in low-income regions where the cost of a borehole is relatively modest if water is at no great depth. Groundwater is also crucial for agriculture and ecosystems equilibriums. It is estimated that groundwater contributes to 38% of the world´s irrigated crop production.
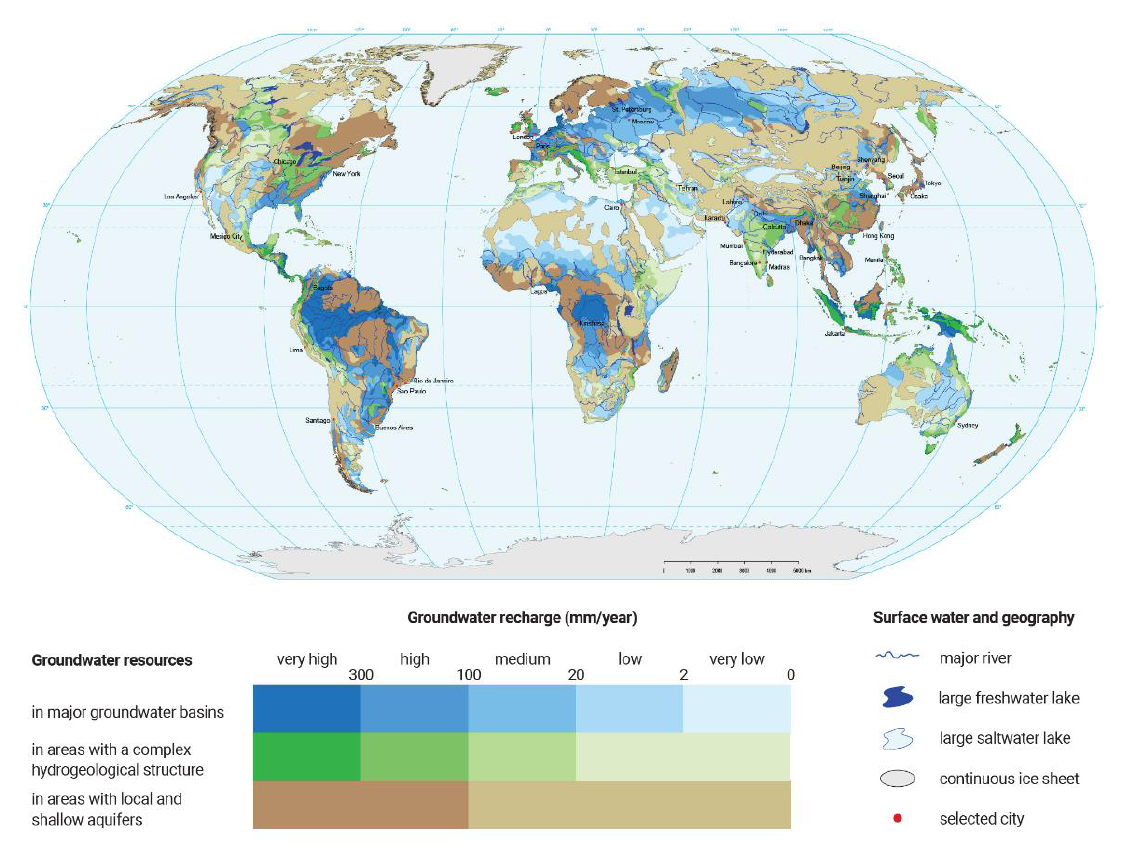
Groundwater resources of the world. Illustration from the United Nations World Water Development Report 2022 (United Nations, 2022)
However, rapid population growth and industrial and agricultural development put increasing pressure on this “hidden treasure”. Urban coverage reducing the aquifer recharge and overexploitation due to intense pumping can result in its dewatering and consolidation, giving rise to ground subsidence and to salt intrusion in coastal aquifers. On the other hand, the entry of pollutants into the aquifer is a very serious threat to water quality due to the great difficulty in removing them.
For more information:
“Engineering, Groundwater, and Integrated Water Resources Management” publication
WFEO Committee on Water website
OCT
2023